Orally Administered UNI-494 Is Well-Tolerated in Dogs
Guru Reddy1, Pramod Gupta1, Atul Khare1, Shalabh Gupta1
1Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.
Background
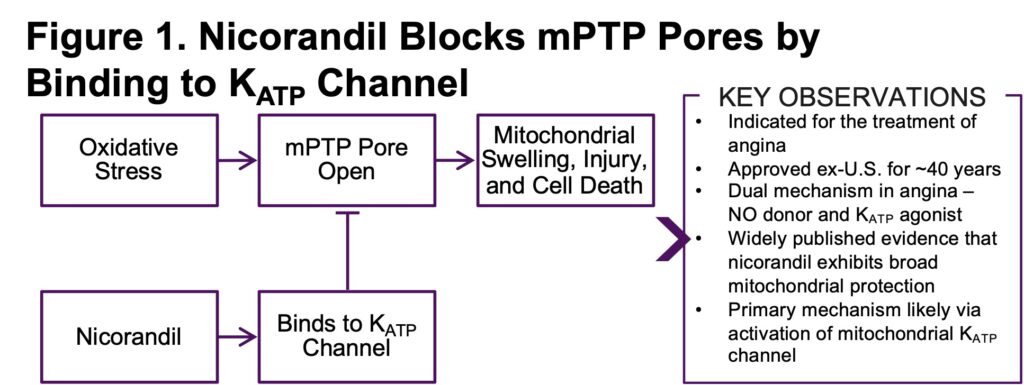
- Inflammation and reactive oxygen species driven mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening causes mitochondrial dysfunction/swelling and eventual cell death over time
- This is implicated in a wide range of acute diseases including acute kidney disease originating from ischemia reperfusion injury or delayed graft function
- Furthermore, unresolved inflammation exacerbates sustained mPTP opening, evident in chronic kidney diseases
- UNI-494 is a selective mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel activator that binds to the KATP channels which reverses the mitochondrial dysfunction by closing the mPTP

OBJECTIVE
We present safety data from a study of UNI-494 in a dog model
Methods and materials
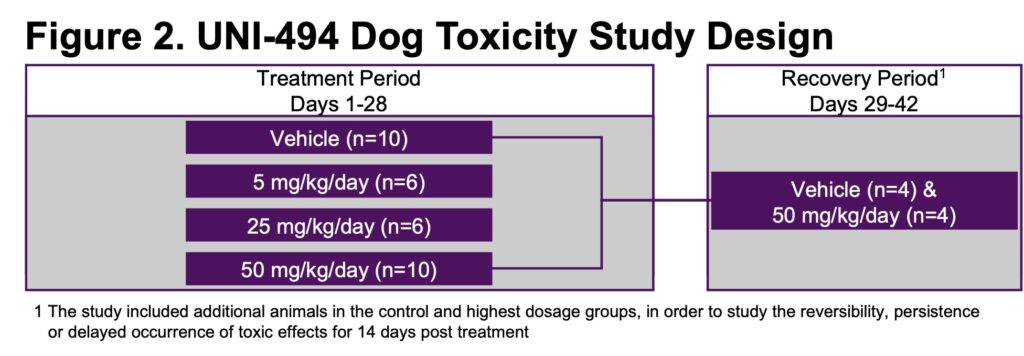
- UNI-494 was administered orally to 32 Beagle dogs over 28 days with a 14-day recovery period (Figure 2)
- Dogs were assigned to 4 groups: 0 (control), UNI-494 5, 25, and 50 mg/kg/day (Figure 2)
- Each group contained 3 male and 3 female dogs, with 2 additional animals of each sex in the control and highest UNI-494 dose groups to assess recovery (Figure 2)
- Safety parameters included in-life observations and measurements (e.g., morbidity/mortality checks, clinical signs, body weight, food consumption, ophthalmological examinations), post-treatment and post-recovery ECG and respiratory parameters, clinical chemistry, urinalysis, coagulation and hematology, toxicokinetic analysis and post-treatment and post-recovery organ weights, macroscopic findings, and histopathology
Results
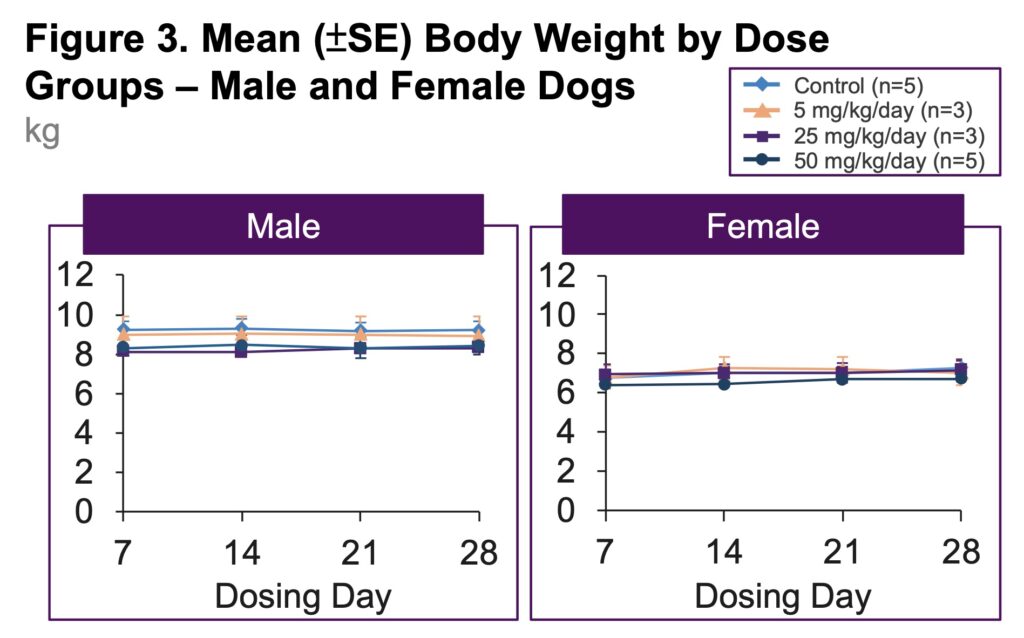
- No adverse UNI-494-related clinical signs, changes in body weight, food consumption, ophthalmological examinations, hematology, clinical chemistry, urinalysis, organ weight, or macroscopic observations were observed in the UNI-494 5, 25, or 50 mg/kg/day dose groups (Figure 3)
- Microscopic changes consisting of vascular wall thickening/perivascular fibroplasia in the heart, acinar cell apoptosis/necrosis in the pancreas, and tubular degeneration in the kidney were observed in the UNI-494 25 and 50 mg/kg/day groups
- There were no unscheduled deaths
- Exposure to UNI-494 (AUC0-t and Cmax) increased in a dose dependent manner over the dose range of 5 to 50 mg/kg following both single and multiple doses for both sexes
- Following both single and multiple administrations, the mean Tmax for all doses of UNI-494 was <1 hour (mean Tmax = 0.235 – 0.826 h). The time to peak concentration of nicorandil was observed earlier for the 5 mg/kg dose (mean Tmax = 0.487-0.997 h) when compared to the 25 and 50 mg/kg doses (mean Tmax = 1.35-2.99 h)

CONCLUSIONS
- UNI-494 was rapidly converted to nicorandil
- UNI-494 exposure increased in a dose-dependent manner
- UNI-494 5 mg/kg/day was well tolerated and was assessed as the No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL)
Implications
- Based on the NOAEL in dogs, the maximum recommended starting dose in humans with a 10x safety margin is 16 mg
- This information should be used to design further efficacy and safety studies of UNI-494
Acknowledgments:
Writing support was provided by Xelay Acumen Group, Inc., and funded by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.