S Gupta1, MD; D Jermasek1, MBA; SJ Hasal1, PhD; S Mourya1; G Reddy1, PhD
1 Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.
Background
- High pill burden and gastrointestinal side effects from phosphate binders (PB) contribute to low adherence to treatment of hyperphosphatemia (HP)1,2
- Oxylanthanum carbonate (OLC), a lanthanumbased PB in development for treating HP in chronic kidney disease (CKD), uses proprietary nanoparticle technology and is formulated in small, swallowable tablets
- In a pivotal open-label clinical trial, OLC was safe and well tolerated

OBJECTIVE
We present new findings on sP levels, pill volume, and pill quantity in patients (pts) with HP treated with OLC compared to their pretrial PB regimen
Methods
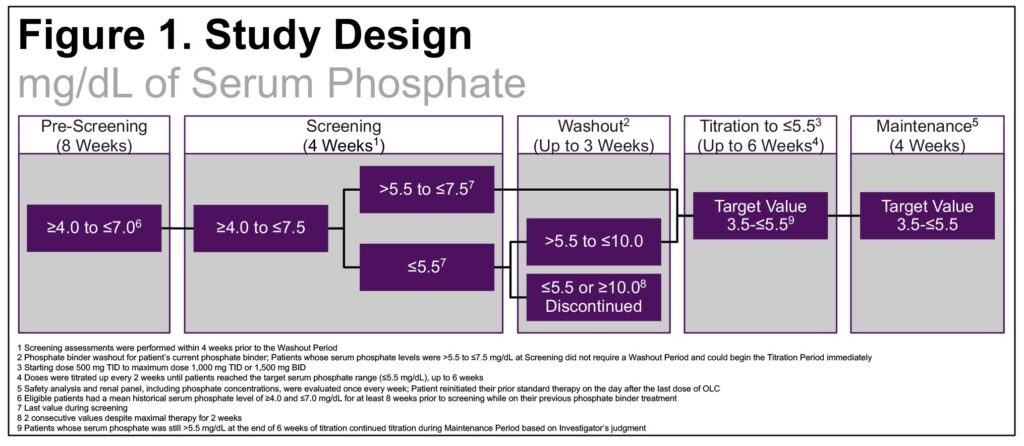
- This open-label, single-arm, multicenter, multidose study enrolled CKD pts on dialysis with mean historical sP ≥4.0 and ≤7.0 mg/dL for ≥8 weeks
- The study consisted of screening, washout, titration, and maintenance periods (Figure 1)
- After washout, pts received OLC 500mg TID, titrated to a max of 1000mg TID over 6 weeks followed by a 4-week maintenance period
- Daily pill volume was calculated by multiplying the pill volume per tablet by the number of tablets per day of pretrial PBs at screening and of OLC tablets at the end of study3
- Pretrial PBs included sevelamer carbonate, calcium acetate, ferric citrate, and sucroferric oxyhydroxide
Results
- Of 128 pts screened, 86 were enrolled; 72 completed the study and had pretrial binder data (Table 1)
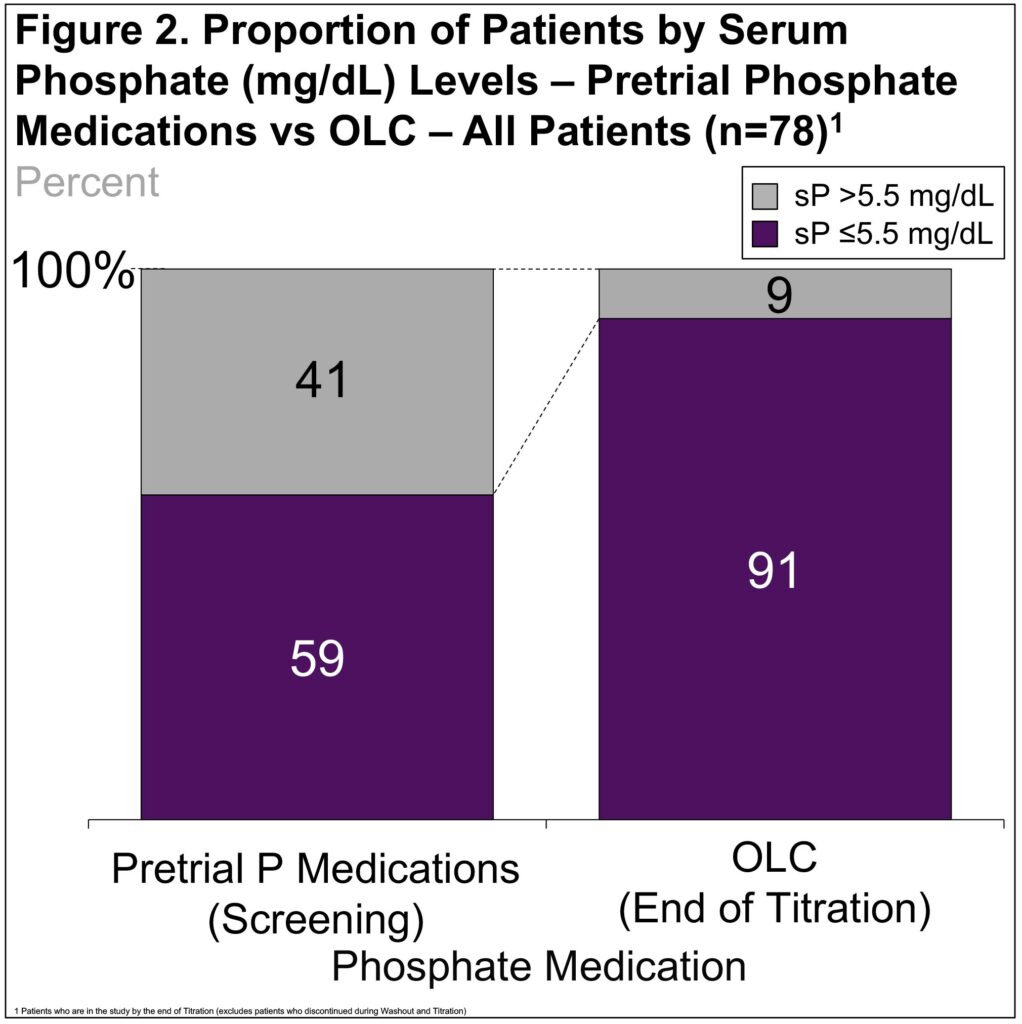
- The sP was ≤5.5 mg/dL at screening in 59% of pts and at the end of OLC titration in 91% of pts (Figure 2)
- The mean daily pill volume of pretrial binders at screening was 9.3 cm3 with a mean of 8.3 pills/day, compared to mean daily pill volume at study end with OLC of 1.3 cm3 with a mean 3.8 pills/day (Figures 3 & 4)
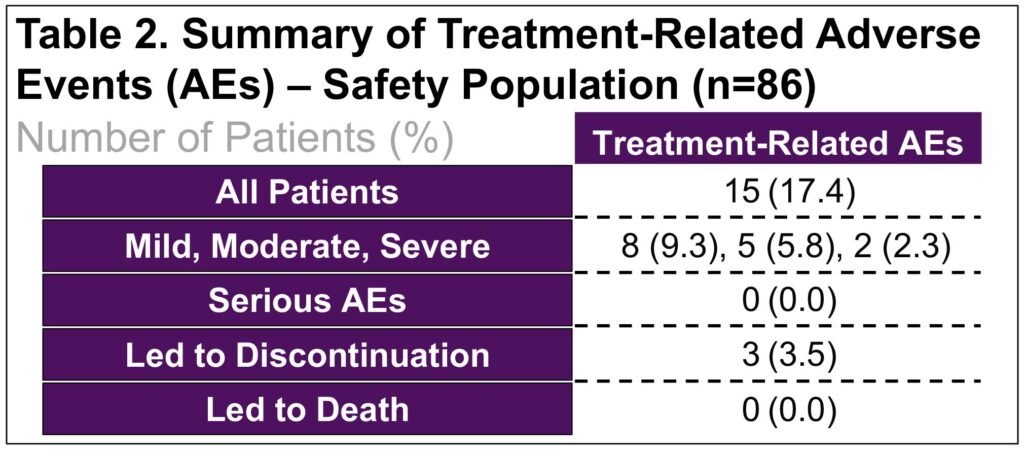
- Severe AEs, as assessed by investigators, were reported in one patient with upper abdominal pain and one with diarrhea
- Reasons for discontinuation during maintenance included adverse events (n=3), investigator decision (n=2), and consent withdrawal (n=1) (Table 2)




CONCLUSIONS
- OLC reduced sP below 5.5 mg/dL in >90% of pts by end of titration
- Mean daily pill volume and pill quantity were significantly reduced with OLC compared to pts’ pretrial PBs
Implications
- Combined with previously presented safety data, these findings suggest that OLC is safe, effective, and well-tolerated
- Its small, easy-to-swallow formulation may be a welcome choice for pts with HP
References
- Chiu YW., et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. Jun.
- Wang S., et al. J Ren Nutr. 2014. Jan.
- Sprague S., et al. Am J Neph. 2023. Jun.
Acknowledgments
Writing support was provided by Xelay Acumen Group, Inc., and funded by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.