Atul Khare1, PhD; Pramod Gupta1, PhD
1Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc., Los Altos, CA
Background
- Over 7 million patients suffer from end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) worldwide1
- Due to low kidney function, patients often become hyperphosphatemic, which leads to an increased risk of death2
- Patients usually rely on dietary restriction and phosphate (P) binders to address hyperphosphatemia
- Current P binders often do not achieve desired levels of P3 and have a high pill burden due to a high quantity of large pills4, 5
- A therapeutic option with a potentially smaller dose volume (i.e., fewer pills and smaller pill size) and efficacy similar to or possibly better than current products would enhance patient quality of life (QoL)
- Lanthanum dioxycarbonate (LDC), RENAZORB, is a novel nanotechnology product that combines lanthanum, which has the highest binding capacity vs. other P binders,6 with a potentially smaller pill size that is swallowed rather than chewed

OBJECTIVE
We present the results of an in-vivo study evaluating the reduction of urine P levels and P/creatinineratios by LDC and sevelamer (SVH)
Methods
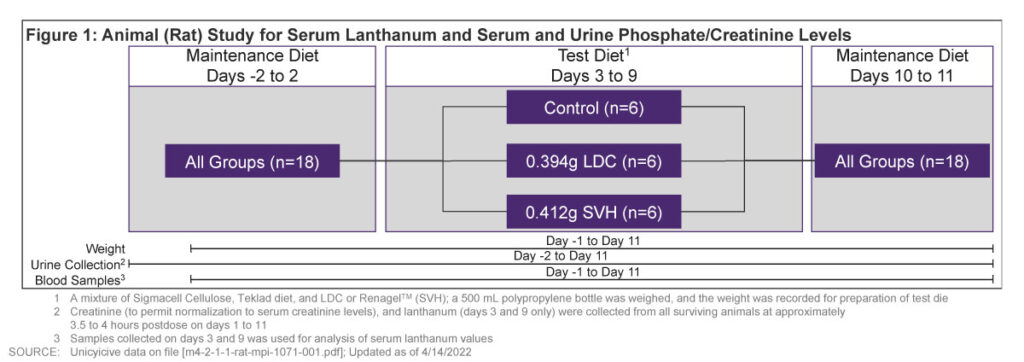
- An in-vivo study evaluated the urine P and creatinine levels by LDC and SVH in healthy rats
- 3 groups (6 rats per group) received control diet, 0.394g LDC/day, or 0.412g SVH/day (LDC and SVH are comparable doses) for 7 days
Results
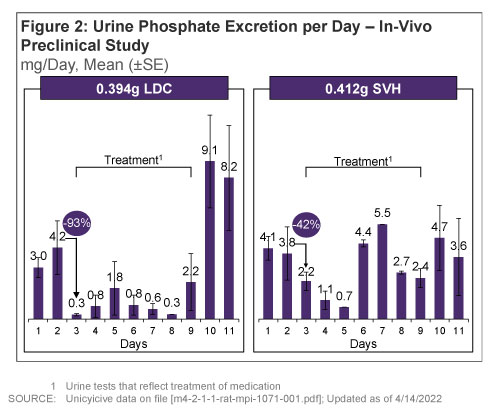
- On day 1, LDC reduced urine phosphate excretion by 93% vs. 42% with SVH (Figure 2)
- LDC reduced urine phosphate excretion throughout the treatment
- LDC has similar decrease in urine creatinine as SVH
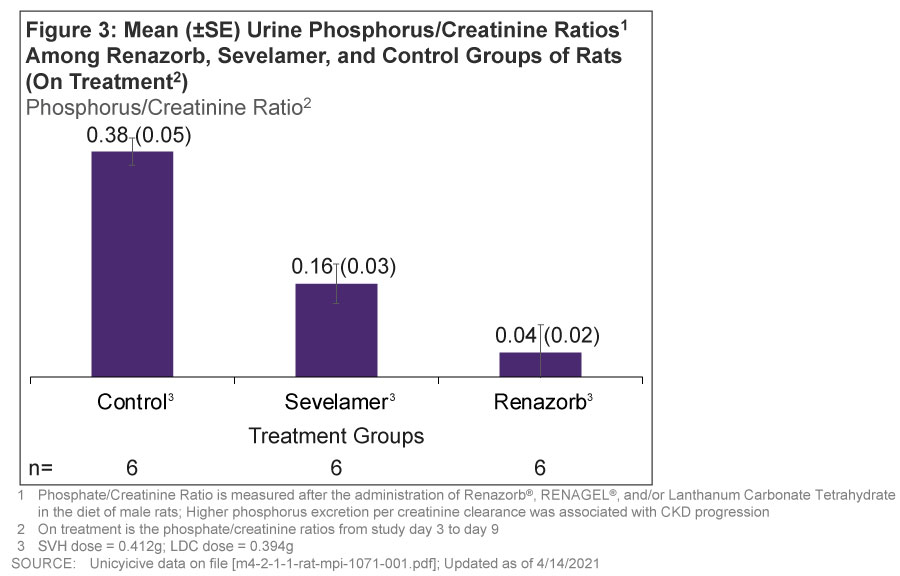
- LDC has more reduction in urine phosphorus/creatinine ratios (0.38) vs. SVH (0.16) or control (0.04) (Figure 3)
- The health of surviving animals did not appear to be affected
- The incidence of animals that did not survive the study duration was similar across groups

CONCLUSIONS
- Lanthanum dioxycarbonate (LDC) demonstrated equivalent or more decrease in urine phosphate excretion vs. sevelamer (SVH)
- LDC showed similar decrease in urine creatinine as SVH
- LDC had more reduction of urine phosphorus/creatinine ratio compared to SVH and control
- All doses of LDC were well tolerated and found safe in rats
IMPLICATIONS
- These results suggest LDC may be a suitable candidate for further development
- Potential benefits of LDC may include reduced pill burden and ease of dose administration (smaller easy-to-swallow vs. chewable), which collectively has the potential to increase patient adherence, improve treatment outcomes, and enhance QoL
References:
1. 991_Lv JC, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019.;
2. 915_Portale AA, et al. Am J Kidney Dis.2014.;
3. 40_DOPPS. DOPPS. 2020.;
4. 983_Chiu YW, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009.;
5. 994_Arenas MD, et al. Nefrologia. 2010.;
6. 1_Daugirdas JT, et al. Semin Dial. 2011.; Xelay Acumen; Updated as of 4/14/2021
Acknowledgments:
Writing support was provided by Xelay Acumen Group, Inc., and funded by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.