Satya Medicherla1, PhD; Guru Reddy1, PhD; Pramod Gupta1, PhD; Glenn M. Chertow2, MD, MPH; Shalabh Gupta1, MD
1Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc., Los Altos, CA; 2Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, CA
Background
- End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) affects >7 million people worldwide1 and ~70% of patients with ESKD have hyperphosphatemia2
- Tenapanor is a sodium/hydrogen exchanger (NHE3) inhibitor that reduces paracellular phosphate absorption by inducing conformational changes in intestinal epithelium3
- Oxylanthanum carbonate (OLC) is an investigational new phosphate binder being developed for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia under FDA’s 505 (b)(2) regulatory pathway
- If approved, OLC will share substantially the same product label and prescribing information as reference-listed drug Fosrenol® (lanthanum carbonate), although OLC tablets are smaller in size and swallowed whole with water and not chewed

OBJECTIVE
This study evaluated effects of OLC+tenapanor on urinary phosphate excretion in rats on a high phosphorus diet
Methods
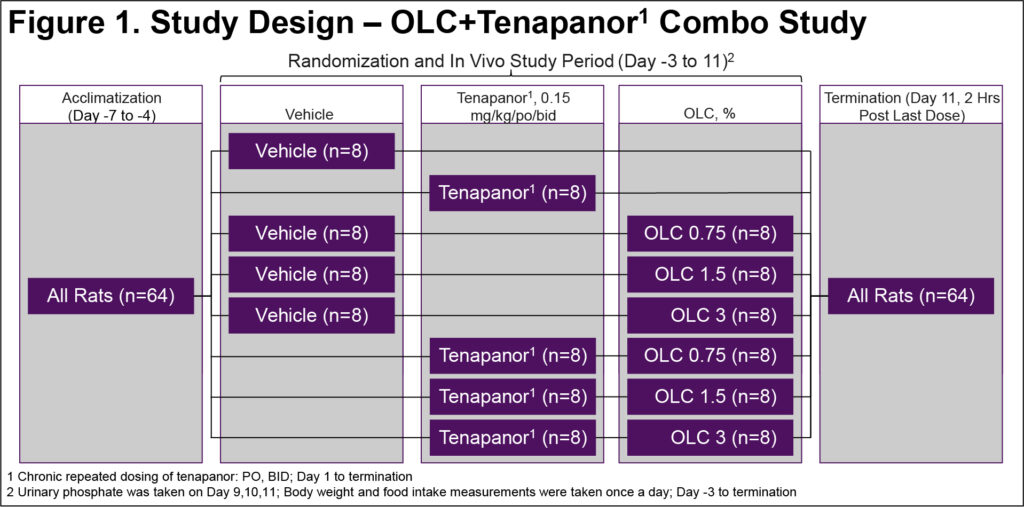
- 64 male Sprague Dawley rats were fed standard chow for 1 week prior to study start and then spiked with additional 0.4% inorganic phosphorus [1:1 sodium:potassium salt, 1.1% (wt/wt) total phosphorus content] for rest of the study3 (Figure 1)
- On study Day -1, animals were randomized into 8 groups (n=8 in each):
- Vehicle
- OLC 0.75%
- OLC 1.5%
- OLC 3%
- Tenapanor 0.15 mg/kg
- OLC 0.75%+tenapanor 0.15 mg/kg
- OLC 1.5%+tenapanor 0.15 mg/kg
- OLC 3%+tenapanor 0.15 mg/kg
- Vehicle and tenapanor were dosed PO twice daily whereas OLC was incorporated into the diets
- 24-hour urine samples were collected using metabolic cages on day 9, 10, and 11 for urinary phosphate measurements
- OLC efficacy data are presented as average of all OLC doses (0.75%, 1.5%, and 3%)
Results
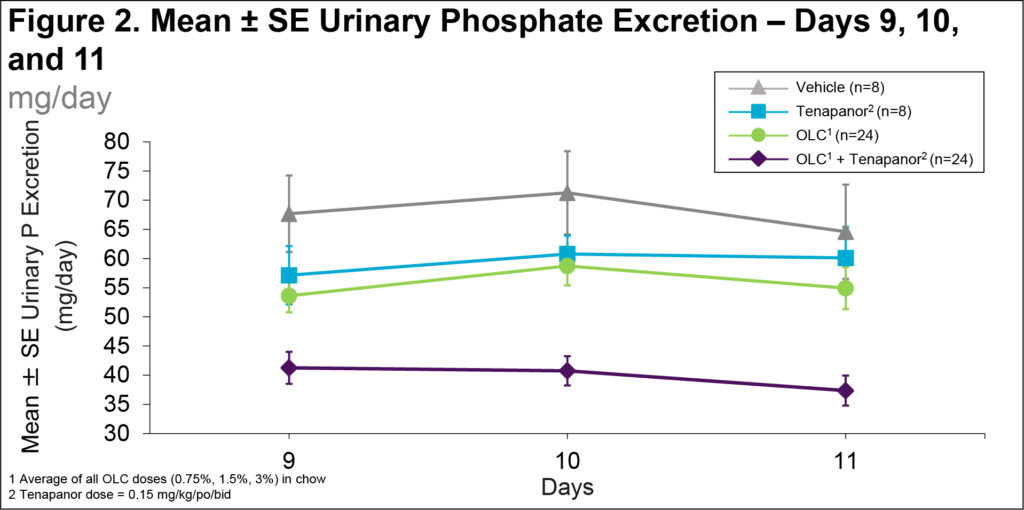
- OLC reduced 24-hour urinary phosphate excretion, with OLC + tenapanor showing lower phosphate excretion compared to vehicle, OLC only, and tenapanor only (Figure 2)
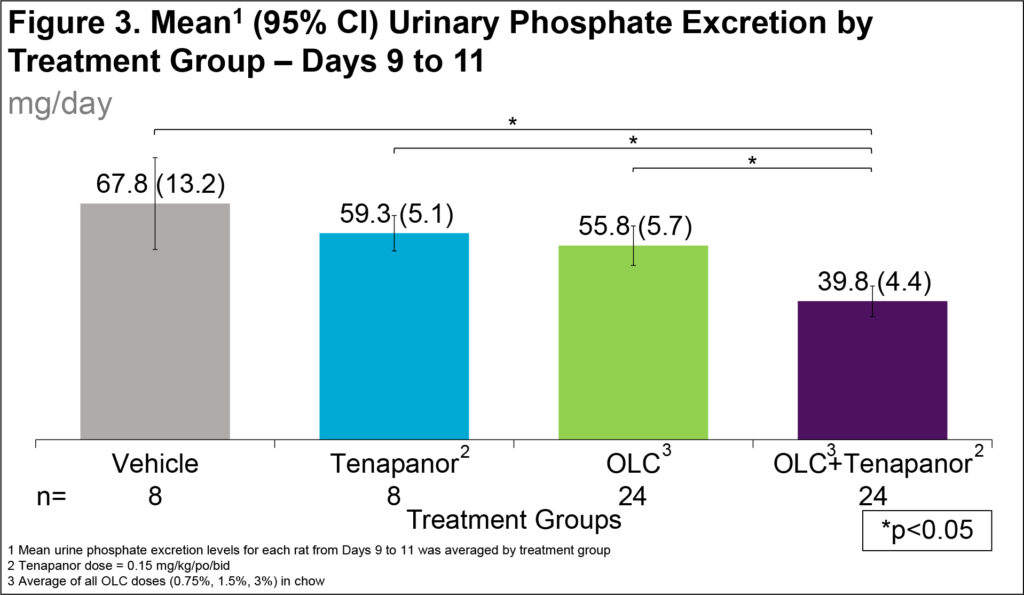
- In tenapanor alone and OLC only groups, urinary phosphate excretion was 8.5 and 12.0 mg/day lower, respectively, compared to vehicle (Figure 3)
- In OLC+tenapanor groups, urinary phosphate excretion was 28 mg/day lower compared to vehicle (Figure 3)
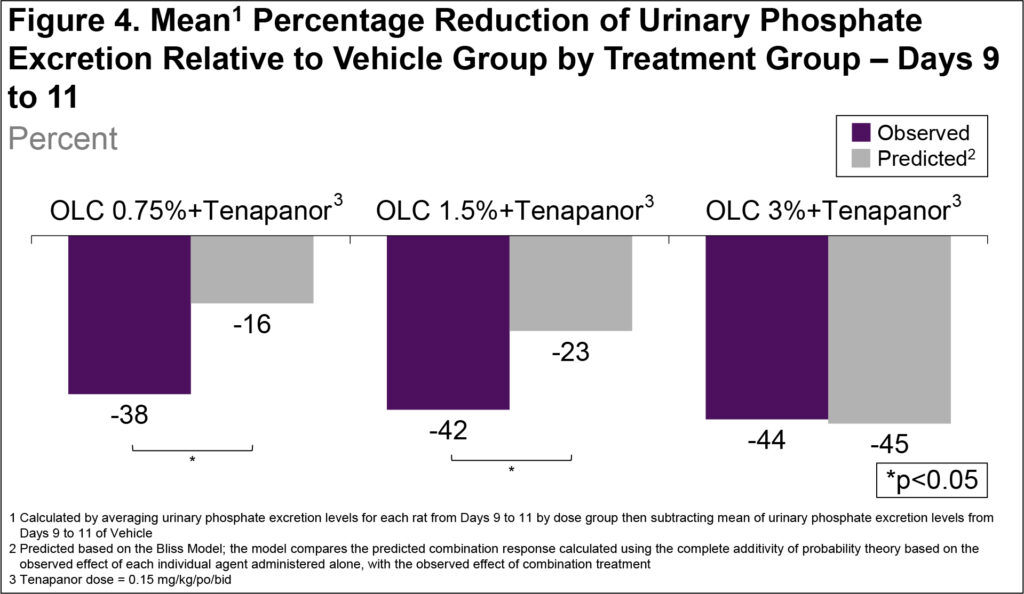
- The observed reduction in urinary phosphate excretion for the OLC+tenapanor groups (0.75% and 1.5% OLC doses) was significantly larger than the predicted reduction based on the single-agent effects in accordance with the Bliss model (Figure 4)

CONCLUSIONS
- This study demonstrated that tenapanor alone modestly decreased urinary phosphate excretion
- OLC alone offered slightly better effects compared to tenapanor alone
- OLC+tenapanor combination achieved a much more pronounced reduction (3.3x greater vs tenapanor alone)
- We demonstrated the potent effects of the novel lanthanum-based phosphate binder OLC and found through Bliss Model analysis that OLC+tenapanor has synergistic, rather than additive, effects in rats
DISCUSSION
- OLC+tenapanor combination exhibited four- to seven-fold more synergistic effects compared to the sevelamer+tenapanor combination4
- The combination of OLC and tenapanor may support a pronounced inhibition of intestinal phosphate absorption by leveraging two distinct mechanisms of action;
- OLC: an intestinal phosphate binder
- Tenapanor: an NHE3 blocker that diminishes transcellular phosphate absorption
- Future studies should evaluate this promising treatment combination in humans with chronic kidney disease
- Additional studies in patients with ESKD and hyperphosphatemia will be required to understand the most effective and best tolerated OLC-containing regimens, as we aim to improve long-term control
References:
1. Lv JC, Zhang LX. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019.
2. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003.
3. King AJ, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2018.
4. King AJ, et al. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021.
Acknowledgments:
Writing support was provided by Xelay Acumen Group, Inc., and funded by Unicycive Therapeutics, Inc.